Research team led by Professor Jo Dong-gyu publishes a paper in Journal of Extracellular Vesicles
- 약학대학
- Hit3679
- 2021-10-18
Professor Jo Dong-gyu's research team has published a new research result that can be applied to the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. The research team confirmed the therapeutic effect in osteoporosis through exosomes derived from adipose stem cells and investigated the mechanism of action that inhibits the differentiation into osteoclasts.
In bone tissue of osteoporotic patients, differentiation of osteoclasts by RANKL is over-activated, and the expression level of Osteoprotegerin, a natural inhibitor of RANKL, is low. In addition, miRNA (microRNA) is an important factor regulating bone function and metabolism, and it has been reported that the expression pattern of miRNA in the serum of osteoporosis patients is different from that of normal people.
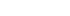
The team confirmed that the decreased bone density was restored when adipose stem cell-derived exosomes were administered to an animal model of osteoporosis induced by resection of the ovaries for two weeks. In addition, it was confirmed that the adipose stem cell-derived exosome inhibits the differentiation of osteoclasts and promotes the migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Component analysis was conducted to identify the mechanism of action of adipose stem cell-derived exosomes, and it was confirmed that Osteoprotegerin and various miRNAs, which are low in expression in osteoporosis, were present in the exosomes. In the case of exosomes deficient in osteoprotegerin, it was revealed that the therapeutic effect of adipose stem cell-derived exosomes was dependent on Osteoprotegerin through the absence of an osteoclast inhibitory effect and no therapeutic effect on osteoporosis. In addition, it was suggested as a new therapeutic target for osteoporosis by confirming that osteoclast differentiation was inhibited when miR-21-5p and let-7b-5p were overexpressed. In addition, it was found that when adipose stem cell-derived exosomes were administered intravenously, they were effectively delivered to bone tissue.
Based on these results, the team presented a potential as a new therapeutic agent for osteoporosis by delivering therapeutic factors to bone tissue using adipose stem cell-derived exosomes in osteoporosis and inhibiting the differentiation of osteoclasts.
Professor Jo Dong-gyu said, “It is speculated that cytokines and miRNAs contained in adipose stem cell-derived exosomes are related to osteoclast and osteoclast differentiation. This study may suggest a new direction for overcoming osteoporosis.”
The research results were published in the October issue of ‘Journal of Extracellular Vesicles’ (IF 25.841), a world-renowned journal. This research was conducted through joint research with Professor Jo Dong-gyu's research team and the research team of Cho Yong-woo of Hanyang University. The research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Hye-sook Lim), Mid-career researcher grant fundedby the National Research Foundation (Chairman Gwang-bok Lee), the Leading Research Center(MRC), and the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety.
Title: Extracellular vesicles from adipose tissue-derived stem cells alleviate osteoporosis through osteoprotegerin and miR-21-5p
Authors: Jeongmi Lee (Ph.D. program, first author), Hakkyun Kim (Ph.D., co-author), Ji-Hoon Han (Ph.D., co-author), Eunae Kim (Ph.D., co-author), Jae-Hoon Seol (Ph.D., co-author), Dong-Gyu Jo (Professor) , corresponding author)